Angular Velocity Calculator
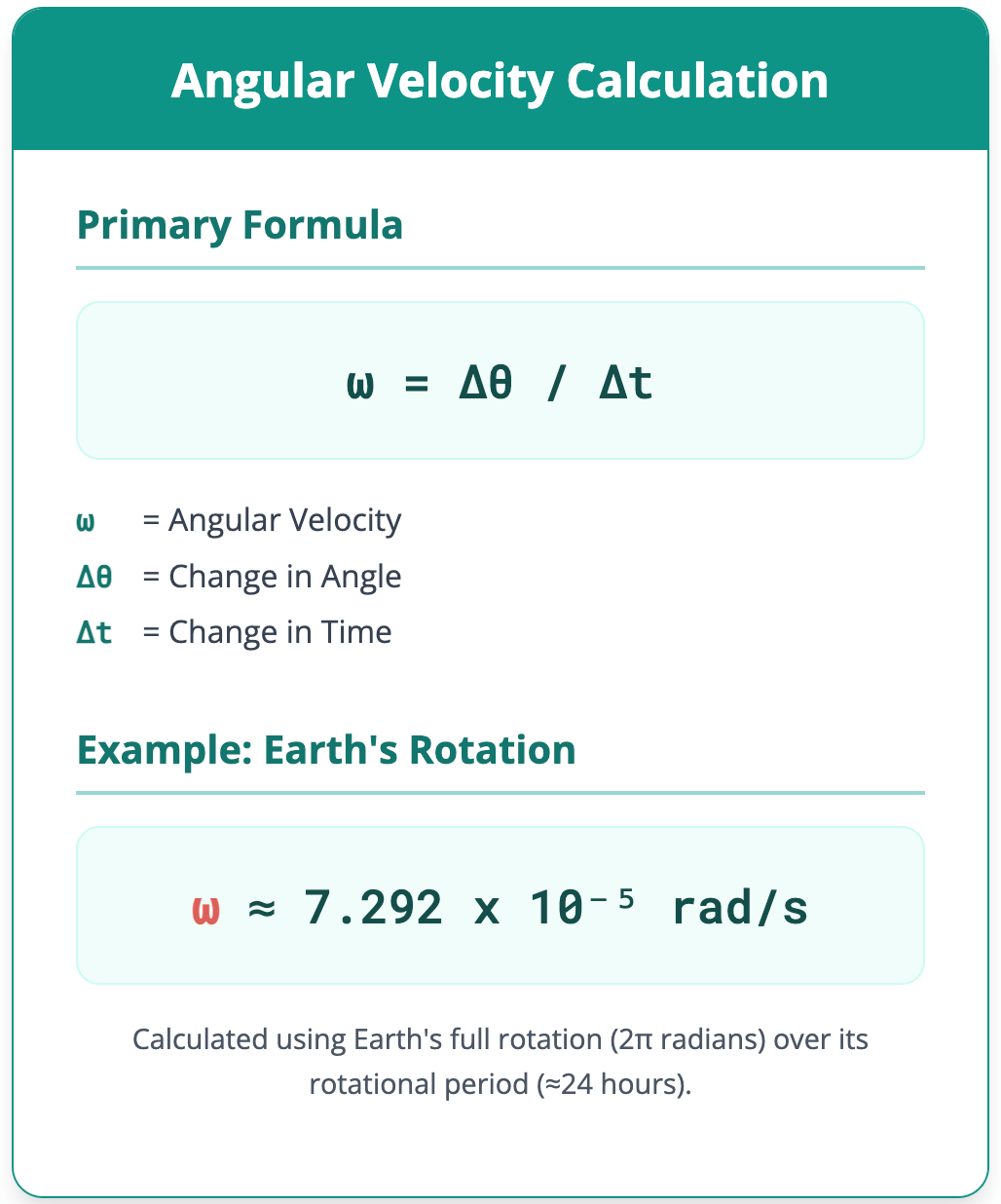
Angular Velocity Calculator Calculate angular velocity from different physical quantities. Calculation Method: Angle Difference Method Radial Velocity Method ω = Δθ / Δt Angle (Δθ) Degrees (°) Radians (rad) Revolutions Time (Δt) Seconds (s) Minutes (min) Linear Velocity (v) m/s km/h ft/s Radius (r) Meters (m) Centimeters (cm) Feet (ft) Angular Velocity (ω) --- Radians per second (rad/s) Degrees per second (°/s) Revolutions per minute (RPM) Angular velocity is the rate at which an object rotates or revolves about an axis, measured as the change in angular displacement over a period of time. To calculate it, the primary formula used
Angle of Elevation Calculator
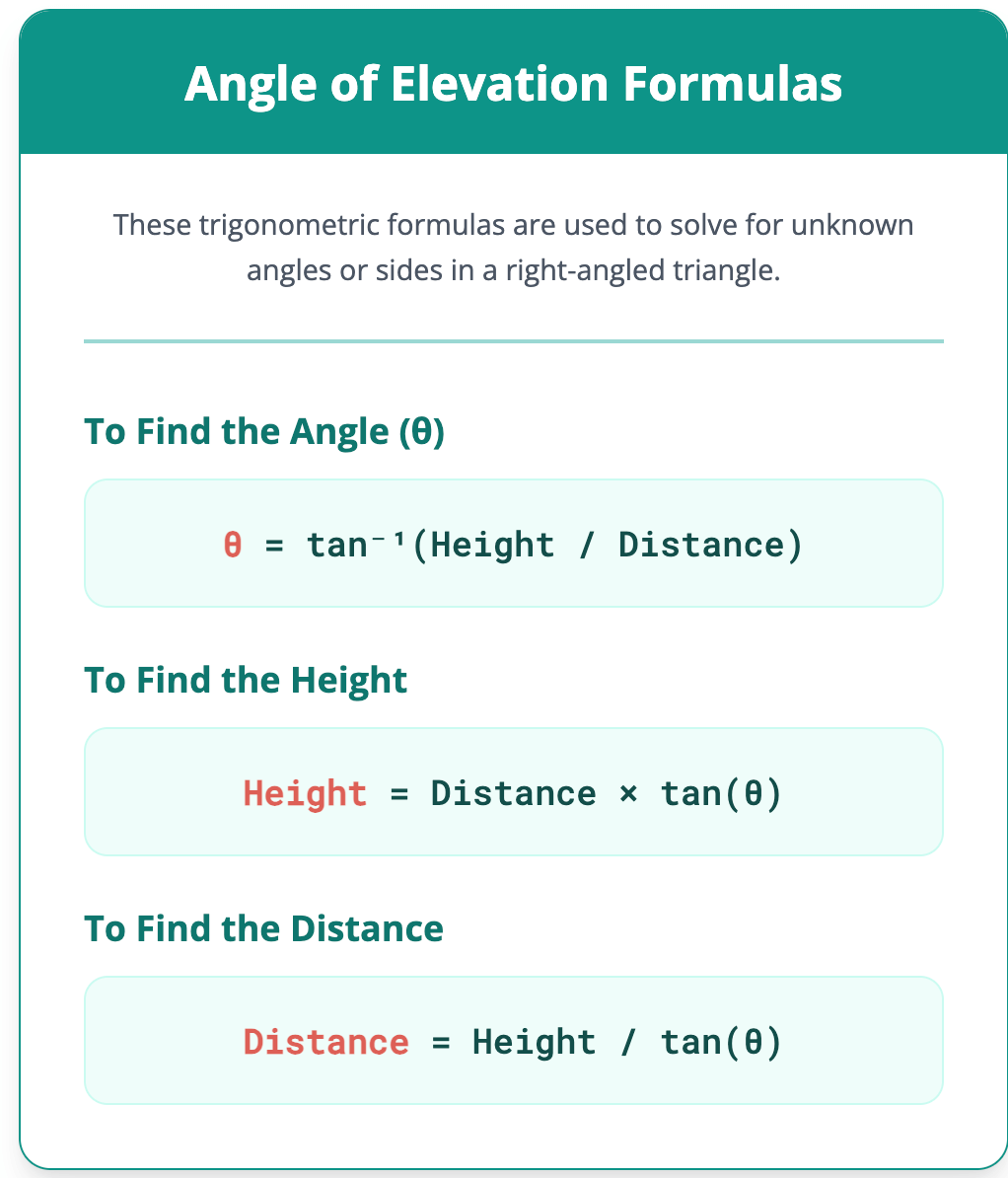
Angle of Elevation Calculator Solve for any variable in a right triangle. I want to calculate: Angle Height Distance Formula θ = tan⁻¹(Height / Distance) Angle (θ) degrees Height meters kilometers feet inches centimeters Distance meters kilometers feet inches centimeters To calculate the angle of elevation, you need to know the vertical height (the opposite side) and the horizontal distance (the adjacent side) from the object. The calculation relies on the trigonometric tangent function. The angle of elevation is found by taking the inverse tangent of the ratio of the height divided by the distance. This relationship is expressed in
Molecules to Moles Calculator
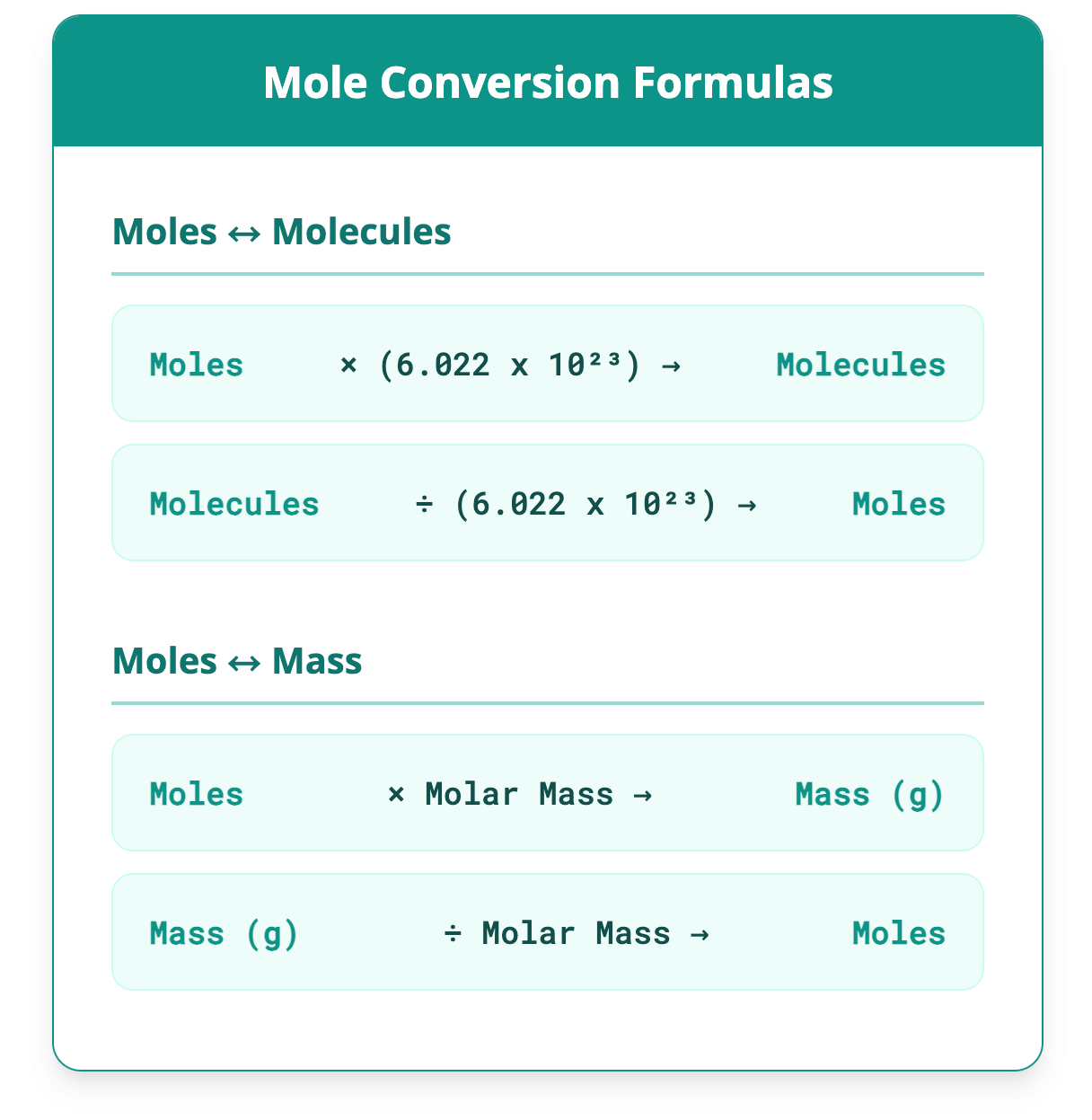
Molecules to Moles Calculator Convert between moles and number of molecules. I want to calculate: Moles Molecules Based on Avogadro's Constant: 6.022 x 10²³ Number of Molecules Number of Moles Mole conversions are a foundational quantitative skill in chemistry that allows for the translation between the macroscopic world of measurable mass and the microscopic world of atoms and molecules. To perform mole conversions, one must understand three core concepts: the mole itself, Avogadro's number, and molar mass. By using Avogadro's number (6.022 x 10²³) as a conversion factor, you can move between the number of moles and the number of
Percent Deviation Calculator
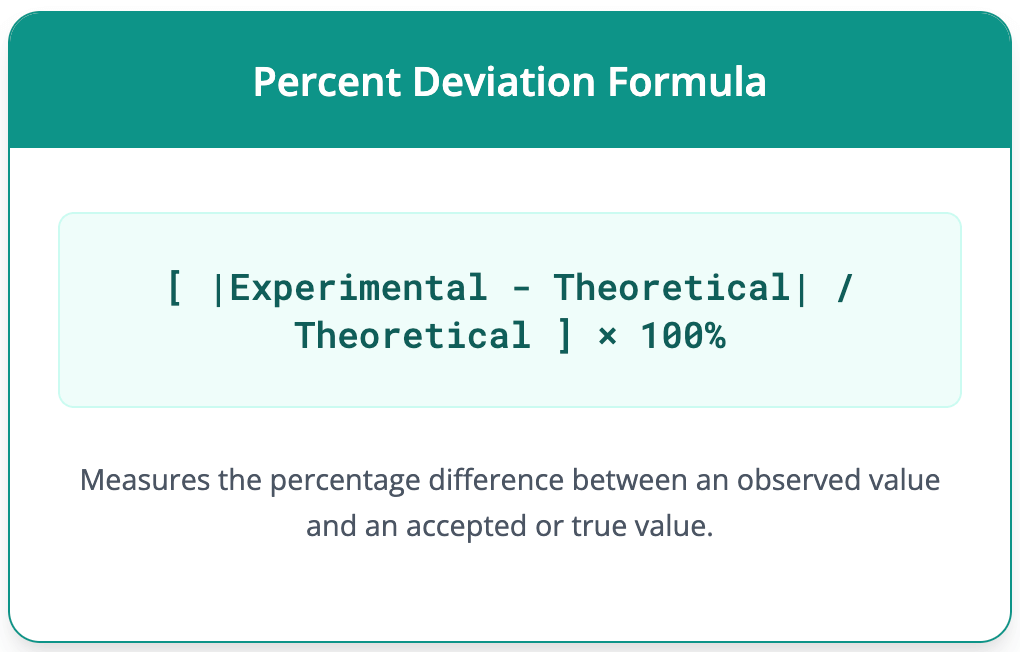
Percent Deviation Calculator Calculate the difference between observed and true values. Percent Deviation = [ |Experimental - Theoretical| / Theoretical ] × 100 Experimental (Observed) Value Theoretical (Accepted) Value Percent Deviation --- To calculate percent deviation, you need two values: an experimental (or observed) value and a theoretical (or accepted) value. The process involves finding the absolute difference between these two values, dividing that difference by the theoretical value, and then multiplying the result by 100 to express it as a percentage. This calculation provides a clear measure of the discrepancy between a measured result and a known standard, which
Marginal Rate of Substitution Calculator
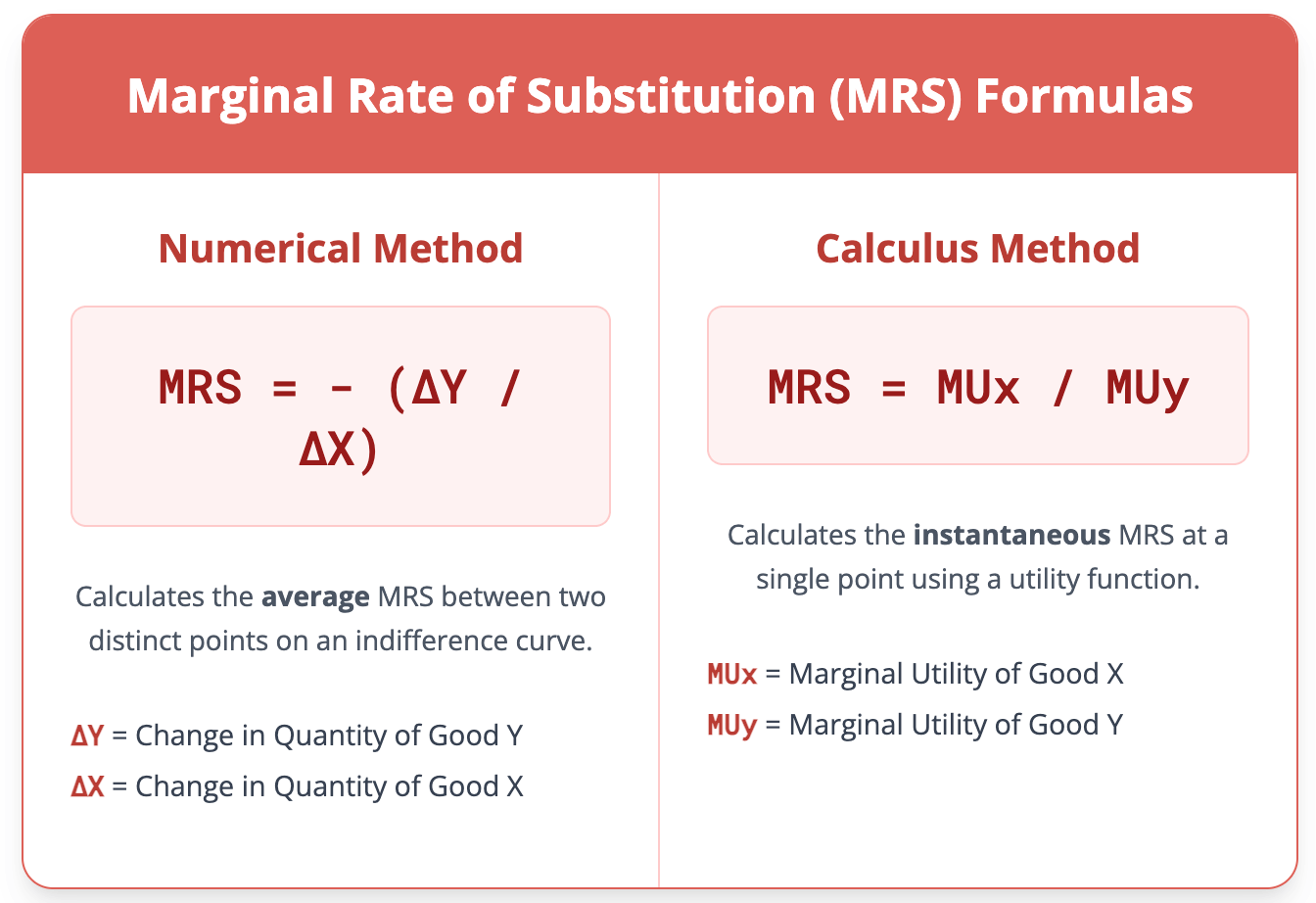
Marginal Rate of Substitution Calculator Calculate the rate at which a consumer substitutes one good for another. Calculation Method Numerical Method (2 Points) Calculus Method (Utility Function) MRS = - (ΔY / ΔX) Good X Initial Quantity (X₁) Final Quantity (X₂) Good Y Initial Quantity (Y₁) Final Quantity (Y₂) Using the Cobb-Douglas Utility Function: U = XaYb Utility Function Exponents Exponent of X (a) Exponent of Y (b) Point on the Curve Quantity of Good X Quantity of Good Y Marginal Rate of Substitution (MRS) --- The marginal rate of substitution (MRS) is a central concept in microeconomic consumer theory
Formal Charge Calculator
Formal Charge Calculator Determine the formal charge of an atom in a molecule. Formula FC = V - N - (B/2) Valence Electrons (V) Non-bonding Electrons (N) Bonding Electrons (B) Calculated Formal Charge (FC) -- Enter the electron counts for a single atom. Formal Charge in Chemistry In chemistry, the formal charge is a theoretical charge assigned to an individual atom within a molecule or ion. It's a tool used to track electron distribution in Lewis structures, helping chemists determine the most plausible or stable arrangement of atoms and electrons when multiple possibilities exist. The concept assumes that electrons in
Turning Radius Calculator
Advanced Turning Radius Calculator Solve for any variable and convert units on the fly. Formula R = L / sin(α) Calculate: Radius Wheelbase Angle Wheelbase (L) meters feet inches Steering Angle (α) deg Turning Radius (R) meters feet inches Designed for quick estimations. Assumes ideal steering geometry. Vehicle's Turning Radius The turning radius is a fundamental measure of a vehicle's agility and maneuverability. In simple terms, it describes the smallest possible circle a vehicle can make when the steering wheel is turned to its maximum limit. A smaller turning radius means a vehicle is more nimble, allowing it to navigate